###异常种类
- 检查性异常: 程序员无法预见,比如打开一个不存在的文件。
- 运行时异常: 可能被程序员避免。
###Exception类的层次
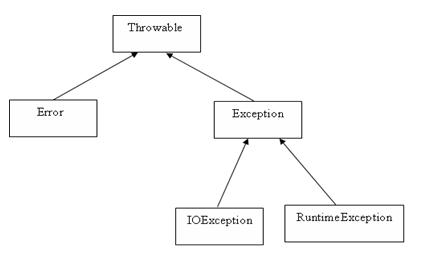
###java内置异常类
Java 定义了一些异常类在java.lang标准包中。
标准运行时异常类的子类是最常见的异常类。由于java.lang包是默认加载到所有的Java程序的,所以大部分从运行时异常类继承而来的异常都可以直接使用。
常见的运行时异常如下表所示:
| 异常 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ArithmeticException | 当出现异常的运算条件时,抛出此异常。例如,除数为0,抛出此类的一个实例。 |
| ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 用非法索引访问数组时抛出的异常。索引为负或大于等于数组大小,则该索引为非法索引。 |
| ArrayStoreException | 试图将错误类型的对象存储到一个对象数组时抛出的异常。 |
| ClassCastException | 当试图将对象强制转换为不是实例的子类时,抛出该异常。 |
| IllegalArgumentException | 抛出的异常表明向方法传递了一个不合法或不正确的参数。 |
| NullPointerException | 当应用程序试图在需要对象的地方使用 null 时,抛出该异常。 |
| NumberFormatException | 当试图将字符串转换成一种数值类型,但该字符串不能转换为适当格式时,抛出该异常。 |
常见的几个检查性异常:
| 异常 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ClassNotFoundException | 试图加载类时,找不到相应的类,抛出该异常。 |
| IllegalAccessException | 拒绝访问一个类的时候,抛出该异常。 |
| InterruptedException | 一个线程被另一个线程中断,抛出该异常。 |
| NoSuchFieldException | 请求的变量不存在 |
| NoSuchMethodException | 请求的方法不存在 |
###异常方法 Throwable 类的主要方法:
public String getMessage()返回关于发生的异常的详细信息。这个消息在Throwable 类的构造函数中初始化了。public Throwable getCause()返回一个Throwable 对象代表异常原因。public String toString()使用getMessage()的结果返回类的串级名字。public void printStackTrace()打印toString()结果和栈层次到System.err,即错误输出流。
###捕获异常
####简单捕获
使用try和catch关键字可以捕获异常。try/catch代码块放在异常可能发生的地方。
try/catch代码块中的代码称为保护代码,使用 try/catch的语法如下:
try
{
// 程序代码
}catch(ExceptionName e1)
{
//Catch 块
}#####实例
import java.io.*;
public class ExcepTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int a[] = new int[2];
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
System.out.println("Out of the block");
}
}结果如下:
Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
Out of the block注意:catch{}之后的语句System.out.println("Out of the block");依然执行。
####多重捕获
一个try代码块后面跟随多个catch代码块的情况就叫多重捕获。
多重捕获块的语法如下所示:
try{
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型1 异常的变量名1){
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型2 异常的变量名2){
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型2 异常的变量名2){
// 程序代码
}###throws/throw关键字
如果一个方法没有捕获一个检查性异常,那么该方法必须使用throws 关键字来声明。throws关键字放在方法名的后面。
也可以使用throw关键字抛出一个异常,无论它是新实例化的还是刚捕获到的。
例如,下面的方法声明抛出RemoteException和InsufficientFundsException:
import java.io.*;
public class Test
{
public void withdraw(double amount) throws RemoteException,InsufficientFundsException
{
// Method implementation
}
//Remainder of class definition
}###finally关键字
finally关键字用来创建在try代码块后面执行的代码块。无论是否发生异常,finally代码块中的代码总会被执行。
实例:
public class ExcepTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[] = new int[2];
try{
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
finally{
a[0] = 6;
System.out.println("First element value: " +a[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is executed");
}
}
}以上实例编译运行结果如下:
Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
First element value: 6
The finally statement is executed注意:
- catch不能独立于try存在。
- 在try/catch后面添加finally块并非强制性要求的。
- try代码后不能既没catch块也没finally块。
- try, catch, finally块之间不能添加任何代码。
###自定义异常 编写异常类时需要记住下面的几点:
- 所有异常都必须是Throwable的子类。
- 如果希望写一个检查性异常类,则需要继承Exception类。
- 如果你想写一个运行时异常类,那么需要继承RuntimeException 类。
###通用异常 Java中定义了两种类型的异常和错误。
JVM(Java虚拟机)异常:由JVM抛出的异常或错误。例如:NullPointerException类,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException类,ClassCastException类。程序级异常:由程序或者API程序抛出的异常。例如IllegalArgumentException类,IllegalStateException类。